ASML 5500 Mask Making Guidelines
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
- Use commercial mask/reticle houses: Photronics, Toppan, Compugraphics, etc. Instruct vendor that this will be used on an ASML 5500/300 system. They have all outer templates for the mask that match our system. You just provide them the data you want printed at wafer scale (1X).
- Reduction is 4X in ASML, mask makers will scale data to 4X size, which will determine price. Scale your mask critical dimensions and tolerances accordingly.
- Masks must be Quartz, should be 0.25” thick.
- Layer-to-layer alignment marks are provided by a calibration mask in our system. No need to put alignment marks on your mask.
- Field Sizes Available (Wafer Scale, 1x):
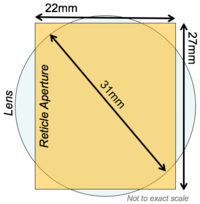
- The full field useable exposure area is limited to the intersection of a 31mm diameter circle and a rectangle of dimensions 22mm x 27mm. See the schematic below for an illustration.
- For High Resolution 0.63 NA: 21mm in X, 21mm in Y
- For 0.4 to 0.57 NA: 22mm in X, 22mm in Y
- Other rectangular sizes available, that fit within the lens/aperture intersection:
- 21mm x 23mm
- 20mm x 24mm
- 19mm x 25mm
- 18mm x 25.5mm
- 17mm x 26mm
- 16mm x 26.5mm
- 15mm x 27mm
- In general, 250nm resolution will resolve over the entire field. Anything smaller than this may not resolve closer to the edges of the field where lens quality degrades, and will also have a smaller viable process window (tolerance of exposure/bake/develop parameters). A number of users have shot ~150nm features.
- Spacing between mask-plate fields : 1mm of Chrome between fields (at wafer scale) in order to blank off unwanted areas.