Difference between revisions of "Packaging Recipes"
m (→Wax-Mounting to Carrier: writing creidts) |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == |
+ | ==[[Dicing Saw (ADT)|Dicing Saw Recipes (ADT 7100)]]== |
| − | === |
+ | ===Recommended Dicing Parameters=== |
| + | This table is for our stocked [https://www.dicing.com Thermocarbon] Resnoid blades. |
||
| + | |||
| + | -4C blades are 4mils/100µm wide, while -8C blades are 8mils/200µm wide. Plan for ~50–100µm extra edge clearance to account for chipping etc. |
||
| + | |||
| + | Narrower (~30-50µm) Nickel Hubbed blades are often used for even narrower dicing streets, these must be purchased by the user. |
||
{| class="wikitable sortable" |
{| class="wikitable sortable" |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 47: | Line 52: | ||
|1-5 |
|1-5 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Quartz |
||
| − | |QuCalculated Blades Exposuresartz |
||
|2.187-4C-30RU-3 |
|2.187-4C-30RU-3 |
||
|25 |
|25 |
||
| Line 77: | Line 82: | ||
|0.5-2 |
|0.5-2 |
||
|} |
|} |
||
| + | |||
| + | ====Anatomy of a Blade==== |
||
| + | Example: '''2.187-4C-9RU-3''' |
||
| + | |||
| + | "2.187": This is the blade Outer Diameter ("OD") in inches (55.56mm). |
||
| + | |||
| + | "4C": Blade thickness in mils. 4mil = 100µm |
||
| + | |||
| + | "9RU": Diamond particle size in microns. Stocked resin blades have embedded diamond particles. Smaller particles create a smoother kerf, but remove less material and are thus less robust or require slower cutting speeds. "RU-3" is a blade parameter that deals with cut quality vs. robustness (lifetime) of the blade. |
||
| + | |||
| + | ===Calculated Blade Exposures=== |
||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
!Blade Diam |
!Blade Diam |
||
!Flange Diam. |
!Flange Diam. |
||
!Blade Exposure |
!Blade Exposure |
||
| + | ! |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|2.187" (55.55mm) |
|2.187" (55.55mm) |
||
|47mm |
|47mm |
||
|4.275mm |
|4.275mm |
||
| + | | |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|2.187" (55.55mm) |
|2.187" (55.55mm) |
||
|49mm |
|49mm |
||
|3.275mm |
|3.275mm |
||
| + | | |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|2.187" (55.55mm) |
|2.187" (55.55mm) |
||
|51mm |
|51mm |
||
|2.275mm |
|2.275mm |
||
| + | |''51mm Currently Unavailable'' |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|2.187" (55.55mm) |
|2.187" (55.55mm) |
||
|52mm |
|52mm |
||
|1.775mm |
|1.775mm |
||
| + | | |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|2.187" (55.55mm) |
|2.187" (55.55mm) |
||
|53mm |
|53mm |
||
|1.275mm |
|1.275mm |
||
| + | | |
||
|} |
|} |
||
| + | |||
| − | === Mounting/Unmounting Samples === |
||
| + | ====Blade Exposure Calculation==== |
||
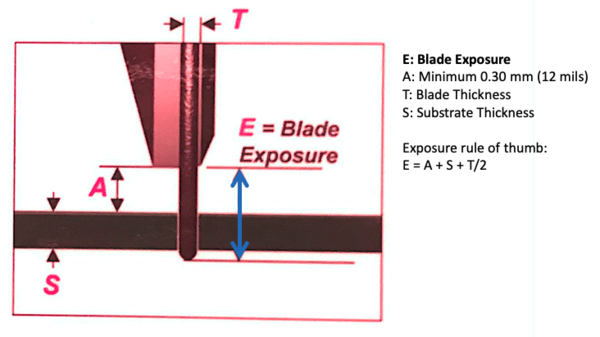
| + | [[File:ADT Dicing - Blade Exposure diagram.png|alt=schematic of blade exposure|none|thumb|600x600px|Diagram of blade exposure. If '''''A''''' '''''< 0.30mm''''', then the flange may hit your wafer, damaging the tool and wafer!]] |
||
| + | |||
| + | ===Mounting/Unmounting Samples=== |
||
The UV-Release Tape dispenser is most-often used for mounting sample for dicing. |
The UV-Release Tape dispenser is most-often used for mounting sample for dicing. |
||
| − | The Tape Model installed is |
+ | The Tape Model installed is Ultron 1042R. [[ADT_UV-Tape_Table_1042R|Data Sheet Here]]. |
| + | |||
| − | * Procedure for mounting sample on UV-Release Tape |
||
| + | *[[ADT WM-966 - UV Tape Mounting Standard Procedure|Procedure for mounting sample on UV-Release Tape]] |
||
| − | * Full Release: 60 sec exposure |
||
| − | * |
+ | *Full Release: 60 sec exposure |
| + | *Partial Release for Shipping: 9 sec exposure |
||
| − | === Surface Protection === |
||
| + | |||
| + | ====Wax-Mounting to Carrier==== |
||
| + | If your final die size will be very small, eg. <3mm square or so, the chances increase that many die will be ejected into the cooling water stream once you begin the 2nd cut angle, because the total surface area of die contacting the adhesive tape becomes very low |
||
| + | |||
| + | A method to overcome this is to mount your sample with CrystalBond wax onto a Silicon carrier wafer. The wax is a much stronger adhesive. The drawback is that you must dissolve the wax to unmount your die, often resulting in a jumbled pile of small die in Acetone/Isopropanol, which can be difficult to handle/sort afterwards. |
||
| + | |||
| + | To mount with wax onto a carrier wafer: |
||
| + | |||
| + | - Prepare a clean silicon carrier wafers, at least ~5mm larger than your sample to be diced. |
||
| + | |||
| + | - The Bay 5 solvent bench is most commonly used for wax mounting, although any solvent bench can be used as long as you cover the hotplate with wax and are careful to clean up any mess. |
||
| + | |||
| + | - Cover the hotplate (cool) with clean tinfoil, and then raise temp to 130-150°C. |
||
| + | |||
| + | - Place the silicon carrier on top, polished wide up, and wait a few min for it to heat up. Pressing down with tweezers can help speed this up. |
||
| + | |||
| + | - Take either a small measured/weighed piece of crystalbond wax, or the whole stick, and touch/press it against the silicon carrier. The wax sticks are stored often on the bench shelves, edge of the bench, or the outside wall of the bench (where the vacuum ports are for the Bay 4 solvent bench). |
||
| + | |||
| + | - Once a large enough puddle of melted wax is produced, remove the wax stick (use tweezers to hold the carrier wafer down), being careful to prevent the wax stringers from landing all over the workspace. You can clean it up later when the hotplate is cold. |
||
| + | |||
| + | — You want to make sure the entire underside of the sample will be contacting the wax, but don’t want so much wax that the sample will be tilted/uneven. Excess wax can easily be removed on an upcoming step. |
||
| + | |||
| + | - With tweezers, place your sample to be diced on the wax, face up. |
||
| + | |||
| + | - Optional: press down the edges/corners of the sample to make it approximately flat. |
||
| + | |||
| + | - Remove the entire tinfoil sheet, with carrier wafer, from the hotplate to let it cool down. Once cool (few mins), remove your silicon carrier with sample attached. |
||
| + | |||
| + | - Optional: To remove wade from the top surface of your sample, or from |
||
| + | |||
| + | the edges, one effective way is to place the mounted assembly onto a POLOS spinner and, while spinning at ~1500-2000rpm, spray with ACE spray bottle for ~30sec, the ISO & N2 dry. This remove wax on the top without significantly attacking the wax mounting between the samples. You could also attempt to use a cotton |
||
| + | |||
| + | swab with ACE, although this is typically much less clean. |
||
| + | |||
| + | - Proceed to apply your surface protection for dicing, eg. Photoresist coating or blue tape etc. |
||
| + | |||
| + | ''Procedure written by Demis D John, 2022-07-04'' |
||
| + | |||
| + | ===Dicing Tips=== |
||
| + | Harder materials will often require larger diamond particle sizes, and thicker blades will last longer if they are overheating and breaking often. |
||
| + | |||
| + | It is not uncommon to have to change a blade in the middle of cutting a wafer - the software is set up to allow this easily without aborting the programmed cuts. The "Height Check Rate" in the recipe will check the blade exposure after this many cuts, using the optical height sensor - this allows you to see how quickly the blade is wearing out (as blade exposure reduces). |
||
| + | |||
| + | Ensuring the cut water jet is hitting at ~7-8 o'clock on the blade and the water jet is being split in two will keep the blade coolest and help prevent breakage. Water sprays should be set to 0.9/0.9/0.9 by default. |
||
| + | |||
| + | For sapphire dicing (very hard material), it is common to use "double-pass dicing", where the substrate is cut at only half depth (eg. cutting only 150µm deep for a 300µm thick substrate) on the first pass, and then re-cut at the full depth. The blade will need to be changed often, so set your "Height Check Rate" to 1 or 2. This can be very time consuming. 200-300µm thick Sapphire substrates are much easier to cut than 650µm thick - often single-pass dicing is adequate for the thinner substrates. |
||
| + | |||
| + | ===Surface Protection=== |
||
| + | |||
| + | ====Photoresist==== |
||
Users most often use sacrificial photoresists to protect the surface from accumulating dicing dust. The static-buildup of dielectric films causes the dust to adhere strongly. Ensure that the PR thickness will adequately coat all your exposed topography (eg. use a ≥2µm thick PR for protecting 1.5-2.0µm tall etched features). |
Users most often use sacrificial photoresists to protect the surface from accumulating dicing dust. The static-buildup of dielectric films causes the dust to adhere strongly. Ensure that the PR thickness will adequately coat all your exposed topography (eg. use a ≥2µm thick PR for protecting 1.5-2.0µm tall etched features). |
||
| − | # Choose a photoresist of appropriate thickness, and spin-coat it & soft-bake it according to a standard recipe. [[Contact Alignment Recipes|Contact Alignment PR Recipes]] [[Stepper Recipes|Stepper PR Recipes]] |
||
| + | #Choose a photoresist of appropriate thickness, and spin-coat it & soft-bake it according to a standard recipe. |
||
| − | # Perform your dicing |
||
| + | ##[[Contact Alignment Recipes|Contact Alignment PR Recipes]] |
||
| − | # Strip the PR in Acetone and ISO & N2 dry |
||
| + | ##[[Stepper Recipes|Stepper PR Recipes]] |
||
| − | == [[Wafer Bonder (Logitech WBS7)]] == |
||
| + | |||
| + | #Perform your dicing |
||
| + | #Remove the die from the UV release tape (60sec UV Exposure) |
||
| + | #Strip the PR from each die in Acetone and ISO & N2 dry |
||
| + | |||
| + | ====Blue Tape==== |
||
| + | Alternatively our low-tack residue-free Blue tape can be used to protect the die surface. Blue tape removal is easy for large die, but does require manual removal from each die, and eliminates sample exposure to solvents. |
||
| + | |||
| + | The very edges of the die may accumulate a bit more dicing dust due to the tape delaminating slightly during dicing. Plan for about 50-100µm of edge clearance on each die. |
||
| + | |||
| + | ==[[Wafer Bonder (Logitech WBS7)]]== |
||
This tool is used for bonding samples to Silicon carrier wafers with CrystalBond wax. |
This tool is used for bonding samples to Silicon carrier wafers with CrystalBond wax. |
||
| + | |||
| − | * [[Logitech WBS7 - Procedure for Wax Mounting with Spin-On Crystalbond|Wax Mounting Procedure, with Spin-On Crystalbond]] |
||
| − | * |
+ | *[[Logitech WBS7 - Procedure for Wax Mounting with bulk Crystalbond Stick|Wax Mounting Procedure, with bulk Crystalbond Wax]] |
| + | *[[Logitech WBS7 - Procedure for Wax Mounting with Spin-On Crystalbond|Wax Mounting Procedure, with Spin-On Crystalbond]] |
||
| + | |||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
Revision as of 17:19, 4 July 2022
Dicing Saw Recipes (ADT 7100)
Recommended Dicing Parameters
This table is for our stocked Thermocarbon Resnoid blades.
-4C blades are 4mils/100µm wide, while -8C blades are 8mils/200µm wide. Plan for ~50–100µm extra edge clearance to account for chipping etc.
Narrower (~30-50µm) Nickel Hubbed blades are often used for even narrower dicing streets, these must be purchased by the user.
| Material | Blade P/N | Spindle Speed
(KRPM) |
Cut Speed
(mm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina, AlN | 2.187-8C-54RU-3 | 25 | 0.5-2 |
| Ceramic | 2.187-4C-30RU-3 | 18 | 0.5-2 |
| GaAs | 2.187-4C-9RU-3 | 35 | 1-5 |
| GaN (<550um) | 2.187-4C-30RU-3 | 35 | 0.5-3 |
| GaN (>550um) | 2.187-8C-30RU-3 | 35 | 0.5-2 |
| Glass/Fused Silica | 2.187-4C-22RU-3 | 25 | 1-5 |
| InP | 2.187-4C-9RU-3 | 35 | 1-5 |
| Quartz | 2.187-4C-30RU-3 | 25 | 1-5 |
| Sapphire | 2.187-8C-54RU-3 | 18 | 0.5-2 |
| Si | 2.187-4C-9RU-3 | 35 | 4-10 |
| Si on Glasss | 2.187-4C-9RU-3 | 25 | 1-5 |
| SiC | 2.187-8C-30RU-3 | 25 | 0.5-2 |
| Ti | 2.187-8C-54RU-3 | 15 | 0.5-2 |
Anatomy of a Blade
Example: 2.187-4C-9RU-3
"2.187": This is the blade Outer Diameter ("OD") in inches (55.56mm).
"4C": Blade thickness in mils. 4mil = 100µm
"9RU": Diamond particle size in microns. Stocked resin blades have embedded diamond particles. Smaller particles create a smoother kerf, but remove less material and are thus less robust or require slower cutting speeds. "RU-3" is a blade parameter that deals with cut quality vs. robustness (lifetime) of the blade.
Calculated Blade Exposures
| Blade Diam | Flange Diam. | Blade Exposure | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.187" (55.55mm) | 47mm | 4.275mm | |
| 2.187" (55.55mm) | 49mm | 3.275mm | |
| 2.187" (55.55mm) | 51mm | 2.275mm | 51mm Currently Unavailable |
| 2.187" (55.55mm) | 52mm | 1.775mm | |
| 2.187" (55.55mm) | 53mm | 1.275mm |
Blade Exposure Calculation
Mounting/Unmounting Samples
The UV-Release Tape dispenser is most-often used for mounting sample for dicing.
The Tape Model installed is Ultron 1042R. Data Sheet Here.
- Procedure for mounting sample on UV-Release Tape
- Full Release: 60 sec exposure
- Partial Release for Shipping: 9 sec exposure
Wax-Mounting to Carrier
If your final die size will be very small, eg. <3mm square or so, the chances increase that many die will be ejected into the cooling water stream once you begin the 2nd cut angle, because the total surface area of die contacting the adhesive tape becomes very low
A method to overcome this is to mount your sample with CrystalBond wax onto a Silicon carrier wafer. The wax is a much stronger adhesive. The drawback is that you must dissolve the wax to unmount your die, often resulting in a jumbled pile of small die in Acetone/Isopropanol, which can be difficult to handle/sort afterwards.
To mount with wax onto a carrier wafer:
- Prepare a clean silicon carrier wafers, at least ~5mm larger than your sample to be diced.
- The Bay 5 solvent bench is most commonly used for wax mounting, although any solvent bench can be used as long as you cover the hotplate with wax and are careful to clean up any mess.
- Cover the hotplate (cool) with clean tinfoil, and then raise temp to 130-150°C.
- Place the silicon carrier on top, polished wide up, and wait a few min for it to heat up. Pressing down with tweezers can help speed this up.
- Take either a small measured/weighed piece of crystalbond wax, or the whole stick, and touch/press it against the silicon carrier. The wax sticks are stored often on the bench shelves, edge of the bench, or the outside wall of the bench (where the vacuum ports are for the Bay 4 solvent bench).
- Once a large enough puddle of melted wax is produced, remove the wax stick (use tweezers to hold the carrier wafer down), being careful to prevent the wax stringers from landing all over the workspace. You can clean it up later when the hotplate is cold.
— You want to make sure the entire underside of the sample will be contacting the wax, but don’t want so much wax that the sample will be tilted/uneven. Excess wax can easily be removed on an upcoming step.
- With tweezers, place your sample to be diced on the wax, face up.
- Optional: press down the edges/corners of the sample to make it approximately flat.
- Remove the entire tinfoil sheet, with carrier wafer, from the hotplate to let it cool down. Once cool (few mins), remove your silicon carrier with sample attached.
- Optional: To remove wade from the top surface of your sample, or from
the edges, one effective way is to place the mounted assembly onto a POLOS spinner and, while spinning at ~1500-2000rpm, spray with ACE spray bottle for ~30sec, the ISO & N2 dry. This remove wax on the top without significantly attacking the wax mounting between the samples. You could also attempt to use a cotton
swab with ACE, although this is typically much less clean.
- Proceed to apply your surface protection for dicing, eg. Photoresist coating or blue tape etc.
Procedure written by Demis D John, 2022-07-04
Dicing Tips
Harder materials will often require larger diamond particle sizes, and thicker blades will last longer if they are overheating and breaking often.
It is not uncommon to have to change a blade in the middle of cutting a wafer - the software is set up to allow this easily without aborting the programmed cuts. The "Height Check Rate" in the recipe will check the blade exposure after this many cuts, using the optical height sensor - this allows you to see how quickly the blade is wearing out (as blade exposure reduces).
Ensuring the cut water jet is hitting at ~7-8 o'clock on the blade and the water jet is being split in two will keep the blade coolest and help prevent breakage. Water sprays should be set to 0.9/0.9/0.9 by default.
For sapphire dicing (very hard material), it is common to use "double-pass dicing", where the substrate is cut at only half depth (eg. cutting only 150µm deep for a 300µm thick substrate) on the first pass, and then re-cut at the full depth. The blade will need to be changed often, so set your "Height Check Rate" to 1 or 2. This can be very time consuming. 200-300µm thick Sapphire substrates are much easier to cut than 650µm thick - often single-pass dicing is adequate for the thinner substrates.
Surface Protection
Photoresist
Users most often use sacrificial photoresists to protect the surface from accumulating dicing dust. The static-buildup of dielectric films causes the dust to adhere strongly. Ensure that the PR thickness will adequately coat all your exposed topography (eg. use a ≥2µm thick PR for protecting 1.5-2.0µm tall etched features).
- Choose a photoresist of appropriate thickness, and spin-coat it & soft-bake it according to a standard recipe.
- Perform your dicing
- Remove the die from the UV release tape (60sec UV Exposure)
- Strip the PR from each die in Acetone and ISO & N2 dry
Blue Tape
Alternatively our low-tack residue-free Blue tape can be used to protect the die surface. Blue tape removal is easy for large die, but does require manual removal from each die, and eliminates sample exposure to solvents.
The very edges of the die may accumulate a bit more dicing dust due to the tape delaminating slightly during dicing. Plan for about 50-100µm of edge clearance on each die.
Wafer Bonder (Logitech WBS7)
This tool is used for bonding samples to Silicon carrier wafers with CrystalBond wax.